Further application examples
Quality control of medical filters
Medical filters consist of fiber bundles with thousands of individual fibers. The filters are surrounded by a filler material at both ends and are trimmed during the process. When the knife's cutting effectiveness decreases, the material can close off the fibers, compromising the filter's optimal effectiveness.
During fully automated inspection, all individual fibers must be recognized, counted, and any closed fibers detected. If the number of closed fibers exceeds a defined value or if these defects are unfavorably distributed geometrically, the filter is rejected. Additionally, analyzing the fiber geometry for constricted, flat, and deformed fibers requires the highest precision from the image processing system.
With lighting optimized for the physical properties of the filters, high-resolution cameras, and special recognition algorithms, the VMT IS/V image processing system achieves exceptionally high detection reliability with maximum availability.
Beyond inspecting the cut surfaces, many other tests have been implemented in the assembly process of medical filters (e.g., assembly inspection, geometry inspection, leak testing, fiber bundle inspection, etc.). VMT image processing solutions are now installed worldwide by this renowned manufacturer. In addition to providing the actual solution, global support was of utmost priority, and VMT can effortlessly meet both requirements with its global presence.
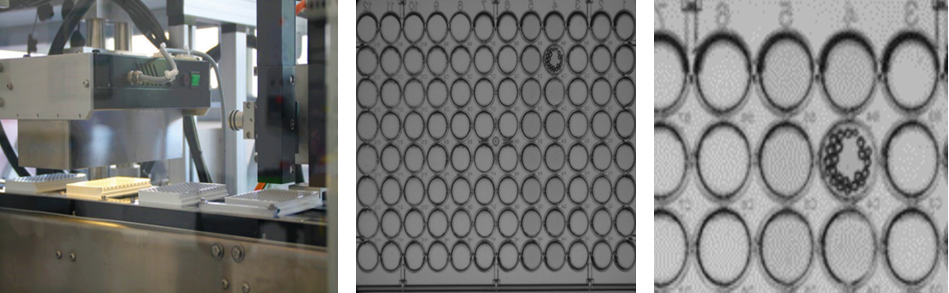
Control of fill levels for microtiter plates – coating processes
Microtiter plates made of polystyrene with curved or flat wells are used as a testing platform in diagnostic laboratories, for example in serology or hematology (blood type identification). The manufacturers of such analytical tests fill the wells of the microtiter plates or strips with the necessary reagents during the manufacturing process (e.g. proteins, antibodies, pathogen components) to load the plastic surface of the wells.

To ensure even loading of the plates or strips, the fill level of the microtiter plates is monitored after filling and checked for possible air bubbles and dirt particles. If any are present, their number and size are analyzed.
Up to 96 wells are measured via transmitted or reflected light with the help of a special camera. Analysis of individual well positions selected by the user is also possible. The plate is removed from the production process if defined cut-off values are exceeded.
Automated inhibition zone measurement for active ingredient tests
Inhibition zones are inspected using indirect transmitted light with an appropriate camera. The insertion and adjustment of the petri dish by the lab technician is followed first by determining the inhibition zone midpoints. The “hole test” procedure determines the midpoint via calculation of the midpoint of the punched hole, while the “cylinder test” procedure relies on measurement of the zone of inhibition itself.
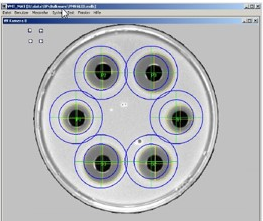
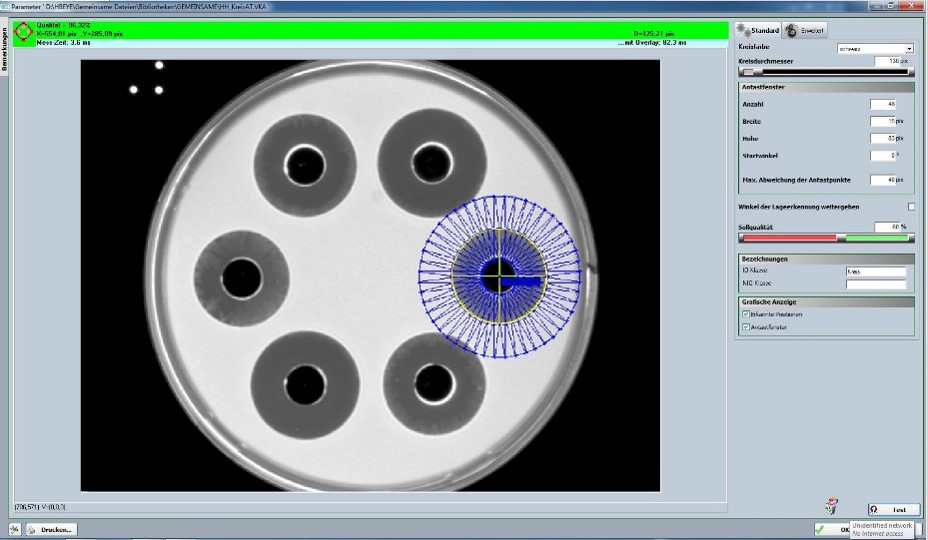
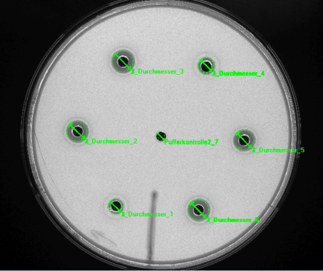
Determination of the surface area of the inhibition zone involves multiple-stage circular ring detection. The diameter is calculated using the measured inhibition zone surface area with an assumed circle approximation. Determination of active ingredient concentration in meeting standards is also possible.

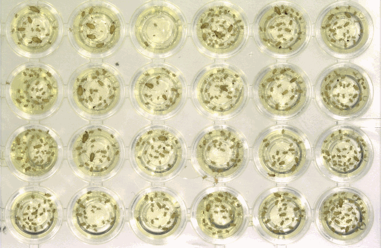
Automated counting aphids
A special VMT inspection solution, which does not necessarily belong to the LifeScience field but is still very unique, is the counting of aphids. Monitoring and evaluating the number of living aphids is important for the production of pesticides. This ensures that during the further development of the pesticide, unnecessary insect deaths are avoided. Instead, their reproduction should be suppressed to prevent further spread. In the research process, a certain number of aphids are placed in TC96 plates. With the help of the VMT inspection solution, it is checked after a certain time whether the number of aphids has increased, remained the same, or if the insects have died.